Fibromyalgia-description and Treatment
 Fibromyalgia is a non-inflammatory suffering which consists in chronic pain, diffuse spread throughout the body, associated with reduced pain threshold and the presence of some specific points, painful pressure and a multitude of other symptoms: fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression, etc.
Fibromyalgia is a non-inflammatory suffering which consists in chronic pain, diffuse spread throughout the body, associated with reduced pain threshold and the presence of some specific points, painful pressure and a multitude of other symptoms: fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression, etc.
Unlike other rheumatic diseases, pain in Fibromyalgia is not localized strictly to the joints and is not accompanied by joint swelling unless occurs in a patient with a rheumatic disease concomitant inflammatory (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis).
Although Fibromyalgia is not a new disease, it has been a long time considered a rheumatism psihogenic based on untreated mental disorders. Only in 1976, introduces the term Fibromyalgia Hench, starting from the term fibrozita used by Gowers in 1904 to describe patients suffering resimteau pain at the touch of light in some points, in the absence of a local inflammations. Subsequently anatomical location is described these painful points will become criteria for classification of the disease.
 Fibromyalgia has traits in common with a number of other sufferings, with whom he is associated, such as: chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, migraine, dismenoreea, as part of a group of diseases characterized by central sensitization.
Fibromyalgia has traits in common with a number of other sufferings, with whom he is associated, such as: chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, migraine, dismenoreea, as part of a group of diseases characterized by central sensitization.
Central sensitization process involves an altering of the mechanisms of pain processing in the central nervous system. This results in an increased sensitivity to pain, which translates into clinical hiperalgeziei appearance (disproportionately big pain girl painful stimulus releaser) and alodiniei (pain triggered by a stimulus that is not harmful and does not normally cause pain-ex. touching).
Painful points from Fibromyalgia are actually a manifestation of alodiniei-the patient describes pain on pressure applied by the doctor in certain areas of the body. Both hiperalgezia and alodinia are based on 2-senibilizarea and peripheral mechanisms. Peripheral sensitization involves an increased sensitivity peripheral receptors (e.g. leather) to pain-as happens for example when we burn the skin.
Central sensitization involves an increase in sensitivity and exciting neurons of the central nervous system. This may be due to increased release of substances stimulating such as substance P, glutamate, aspartate (which leads to increased levels of calcium inside the nerve cell) and also decrease the amount of chemicals with inhibitory role of pain such as GABA (gaba-acid aminobutyric acid) or serotonin.
Functional changes in the brain of the patient with fibromyalgia have been studied in recent times using modern neuroimaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance (MRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET), emphasizing multiple abnormalities of the downward tracts of pain (the ones that go to the brain toward the periphery), as well as reducing blood flow and neural activity in certain brain areas involved in pain processing.
Also, there is a connection between chronic pain and sleep disorders. Electroencephalographic studies performed during sleep, they show that in patients with fibromyalgia, poor quality of sleep (non-REM-sleep without dreams, disrupted where alpha) is associated with persistent pain, intepeneala emphasized.
It was found that patients with fibromyalgia have a dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal gland. The three structures (hypothalamus, pituitary gland and the adrenal glands), based on hormones, are involved in controlling the organism response to stress. Patients with fibromyalgia have a low response to the stress axis, translated by low levels of cortisol and growth hormone.
The causes are not fully known. It has been observed that many patients with fibromyalgia report the onset of symptoms after a traumatic event or physical stress. There is also a tendency for aggregation of disease, family support, especially on the native line. There were some infectious agents and incriminati as triggers but the connection between them and the disease could not be demonstrated.
Risk factors are the female sex, age (most commonly occurs between 20-55 years, but the prevalence increases with age), family history, psychosocial stress, inflammatory diseases coexisting-rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc., the presence of mental disorders, physical injuries.
Table of contents
- Fibromyalgia-General description
- Fibromyalgia: symptoms
- Radioimagistice and laboratory investigations
- The diagnosis of fibromyalgia
- Treatment
- Fibromyalgia: Evolution, Complications
- Medical Recommendations

Fibromyalgia: symptoms
The main manifestation of the disease is pain. The disease starts slowly, initially being only a localized pain (cervical, lumbar column), later to become diffuse. This diffuse pain affects both sides of the body-both the upper and lower part, including and the axial skeleton. Pain does not follow a typical distribution on a certain nervous territory but may be accompanied by disturbances of sensitivity (numbness, tingling, sensation of heat or cold, local time). The patient bone or muscle pain assigned, noting a worsening to stress, physical exertion, lack of sleep, climate changes. Symptoms may be exacerbated in the morning, accompanied by redoare, intepeneala morning and after prolonged rest that can be over 1 hour, similar inflammatory joint diseases. Fatigue can dominate the picture, with the non-refreshing sleep. Generally, the symptoms are variable intensity, but tend to become more pronounced, leading to marked up functional impotence, affecting normal social life. While the patient may associate mood disorders, anxiety and depression.
According to intenstitatea these three symptoms-pain, anxiety and depression, a study conducted in 2003 by Giesecke and collaborators, fibromyalgia patients divided into 3 categories:
1) those with the lowest levels of pressure sensitivity with high threshold of pain, moderate anxiety and depression
2) those with increased susceptibility and increased levels of anxiety, depression
3) those with increased susceptibility to pain but with good control of pain and low levels of anxiety and depression
Other associated clinical manifestations are varied and are interested in multiple organs and systems of the body:
-digestive system: nausea, gastric acidity, pronounced intestinal transit disorders-diarrhea, constipation, chronic abdominal pain, bloating, vomiting
-Genitourinary system: chronic pelvic pain, cystitis (bladder wall inflammation), frequent urinations common, painful, in the absence of other causes of pain during menstruatiilor
-cardio-respiratory system and peripheral vascular: non-cardiac chest pain, rapid pulse, breathing disorders during sleep, Raynaud's syndrome
-eye-sight disorders, ocular dryness
-neuropishic-migraine, chronic headaches, sleep disorders, difficulty concentrating and memory disorders, depression, anxiety, restless legs syndrome, etc.
-skin-dry skin, itching, rash and drizzle.
Radioimagistice and laboratory investigations
There are no laboratory or radiological tests. Tests are performed to rule out other diseases that may debut in a similar way: complete blood count, VHS, C-reactive protein, liver and kidney samples, muscle enzyme CK, LDH, serum electrolytes-sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, especially hormones-thyroid, rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies only if signs and symptoms are suggestive for lupus, polyarthritis, or dosage of vitamin D. For a proper diagnosis must be excluded inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, polimialgia, etc.., endocrine diseases, infections, malignancies. In Fibromyalgia all tests mentioned above are generally in the normal range. Very great care must be taken when testing unnecessary and the rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibodies, in the absence of clinical manifestations suggestive, archaelogists that both tests can be positive in a significant number of otherwise healthy people.
For a proper diagnosis must be excluded inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, polimialgia, etc.., endocrine diseases, infections, malignancies. In Fibromyalgia all tests mentioned above are generally in the normal range. Very great care must be taken when testing unnecessary and the rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibodies, in the absence of clinical manifestations suggestive, archaelogists that both tests can be positive in a significant number of otherwise healthy people.
The diagnosis of fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia: diagnosis, physician rheumatologist relies on ACR 1990 criteria for the classification of the disease (criteria designed mainly for clinical trials, to select homogeneous patient populations).
In time they came into clinical practice but there is a certain boundaries of these criteria, mainly related to the variability of the disease both from patient to patient, and from the same patient from day to day. According to these criteria, the patient with fibromyalgia must present pain lasting more than three months, on both sides of the body, the right and left upper and lower class, including and the axial skeleton (cervical, thoracic column, lumbar).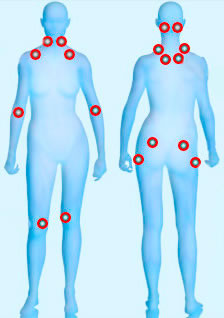
You also need to submit to pain to at least 11 of the 18 points, palpate the physician. These points are symmetrically distributed on both sides of the body at the level of: occiputului, cervical, supraspinatus, trapezius, anterior lateral Coast 2, elbow, hip, side gluteal, medial knee.
There are controversies here variable pressure applied when doctors examined the patient, that the pain of patients with fibromyalgia is not limited only to these areas tested and also the fact that there are people that do not suffer from Fibromyalgia may feel pain from the pressure. Another issue of the ACR criteria is as old does not include major symptoms of the disease such as-sleep disorders, fatigue or depression.
The proposed new criteria of diagnosis keeps the pain broadcast lasting more than 3 months but have replaced the painful points with a list of symptoms you need to be confirmed by patient and physician graduated, including diffuse pain index (WPI-Widespread Pain Index) and the severity of symptoms Scale (SSS-Symptom Severity Scale). In WPI-the patient is made to indicate areas of maximum, 19, in the last week, each receiving 1 point area. In SSS-4 category-non-refreshing sleep, fatigue, cognitive and somatic symptoms disorders (cardiovascular, digestive, urinary, etc.) I get points from 1-3 (0-No 1-symptoms, flashing light, 2-moderate, 3-persistent, severe), racking up a maximum of 12 points. WPI diagnostic must be over 7 and SSS over 5 or 3-6 WPI with SSS over 9.
Treatment
 There is no treatment to cure the disease. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms and improve health. A correct approach involves the use of non-pharmacological methods and pharmacological tests depending on the intensity of pain and associated symptoms. Non-pharmacological methods include: hidrokinetotherapy, graduated exercise, relaxation techniques, massage, physiotherapy, psychotherapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
There is no treatment to cure the disease. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms and improve health. A correct approach involves the use of non-pharmacological methods and pharmacological tests depending on the intensity of pain and associated symptoms. Non-pharmacological methods include: hidrokinetotherapy, graduated exercise, relaxation techniques, massage, physiotherapy, psychotherapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
The patient must be informed that it is possible that initially, the commencement exercises, the pain to become more pronounced. The work should not be interrupted, however. There are studies that show that patients with fibromyalgia who do move (aerobic gymnastics, gymnastics in water-basins with warm water, stretching, swimming, walking or bicycling), have a better evolution.
An important role in the treatment of fibromyalgia: has the patient himself. He must adopt a new life style, trying to avoid the stress, to devote sufficient time to rest and sleep, continue or begin a regular exercise program (together with fiziokinetoterapeutul devise a plan of exercises that can be performed at home), to maintain a healthy nutrition.
Alternative therapies seem devoid of risks and can be considered as adjuvant therapy in pain control and the level of stress: acupuncture, qigong, yoga and tai-chi. Tai-Chi can be a solution for people who cannot do more intense exercise.
Pharmacological treatment varies depending on the clinical manifestations.
For pain control, using painkillers-acetaminophen (paracetamol), with or without tramadol, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g. Naproxen, Ibuprofen, etc.). Not recommended using glucocorticoizilor and strong opioids. Also there are no studies supporting the benefits of long-term use of non-steroidal antiinflamatoarelor.
For pain and fatigue can use antidepressants reuptake inhibitors of serotonin-and norepinephrine-Duloxetine, Milnacipran, tricyclic antidepressants-amitriptyline, selective inhibitors of serotonin-reuptake Fluoxetine-to improve sleep. The effect of tricyclic antidepressants in Fibromyalgia is independent of antidepressant action, smaller doses being used (e.g. Amitriptyline 25 mg per day).
Unfortunately the digestive adverse reactions and reduce the use of these neuropsychiatric drugs. Dual reuptake inhibitor of serotonin and norepinephrine have looks similar efficiency with tricyclic antidepressants, with no adverse reactions. The most common side effects are nausea and headache. Duloxetine is administered orally per day initially, cate: active: after 1 week dose can grow to 60mg/day. Milnacipran is given all the form how many oral 25 mg/day, then 25 mg twice a day and maintenance dose is 50 mg 2 times a day. Both drugs have been approved in the U.S. for the treatment of fibromyalgia:.
Anticonvulsants-Gabapentin, Pregabalin are used for controlling certain types of pain, including that of fibromyalgia pregabalin-being the first drug approved in the U.S. for the treatment of fibromyalgia:. Effectiveness of these medications is due to the effect of Alpha2 subunits delta calcium channel voltage dependent on the level of neurons. The consequence is a reduction in nerve cell calcium penetration and secondary loss of neurotransmitatoare as well as the release of glutamate and substance P.
Other drugs found on list of EULAR (European League Against Rheumatism) treatment of fibromyalgia: are: dopamine agonist Pramipexole-(acts like dopamine in the brain) being a drug used primarily in neurology to treat Parkinson's disease, Tropisetron-serotonin receptor antagonist, Ondansetron cousin, used mainly as an emetic (to treat nausea and vomiting after chemotherapy) with analgesic effect.
Fibromyalgia: Evolution, Complications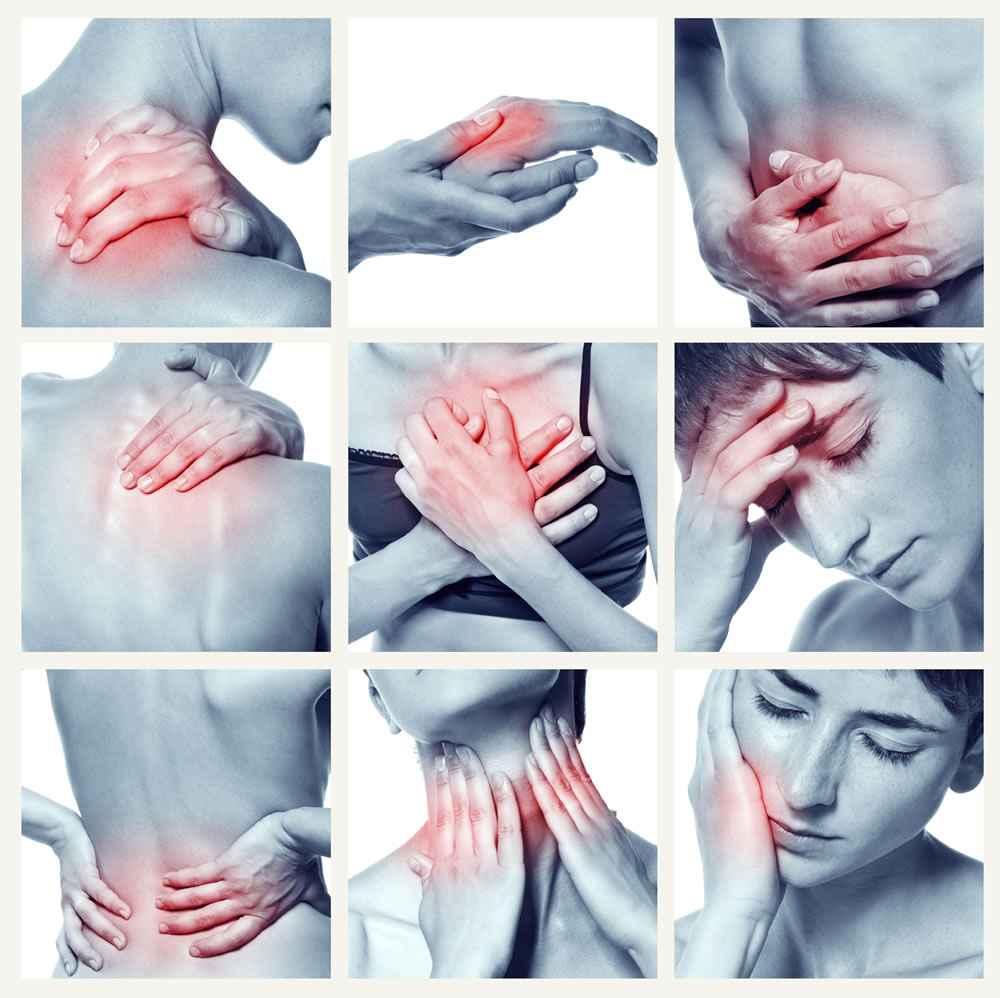
In general, fibromyalgia is a chronic condition, with long, no curative treatment. Studies have shown that treatment can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life of these patients secondary.
Factors that predict a more severe are the presence of a traumatic event trigger physical or psychic, severe disability, treatment received in special units (as opposed to integrated in community patients having a better evolution), the large number of doctors who have consulted the patient until the diagnosis (involves a delay in diagnosis and treatment).
Although symptoms of fibromyalgia varies as intensity and severity, altering physical function and emotional impact of disease decrease quality of life in almost all patients. Nearly half of patients with fibromyalgia difficulty to perform daily activities-require a longer time in order to mobilize in the morning, it is difficult to carry out activities that involve lifting weights or sustained, repetitive movements, walking distance to go higher.
Some patients arrive to escape from light objects and hand to fear of movement. Nearly one-third are forced to quit or change jobs. Family support, lack of friends and intimates has a negative impact on the evolution of the disease.
Medical Recommendations
As mentioned Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition in which the remission of spontanta rarely appears. That's why a very important role in the evolution of the disease, educating the patient has. He needs to understand that although the disease is long, you can have a good quality of life, adopting a positive attitude and developing together with experts ways to cope with suffering.
There is no single treatment for all patients with fibromyalgia. The correct approach is the one involving a multidisciplinary team of specialists. A negative attitude to the false hope of the patient and that a certain drug will solve all of the symptoms of the disease, darken the prognosis.
Rheumatologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, Doctor of rehabilitation and Soccer
-Analgesics: Acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents: Tramadol, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Diclofenac, Aceclofenac, etc.
-Antidepressants: Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine, Duloxetine, Milnacipran
-Anticonvulsants: Pregabalina
-Antiparkinsoniene: Pramipexole
– Natural Supplements: Sinohial, Probioflora powder (treat intestinal flora for regulating immunity), Rheumaflex cream, gel, spray and capsules, Rattle & ginseng, Passiflora, Rosemary.
Qigong Fibromyalgia here Diet here and Acupuntura.













Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!